
Benefits of multilayered printed circuit boards
Benefits of Multilayered Printed Circuit Boards
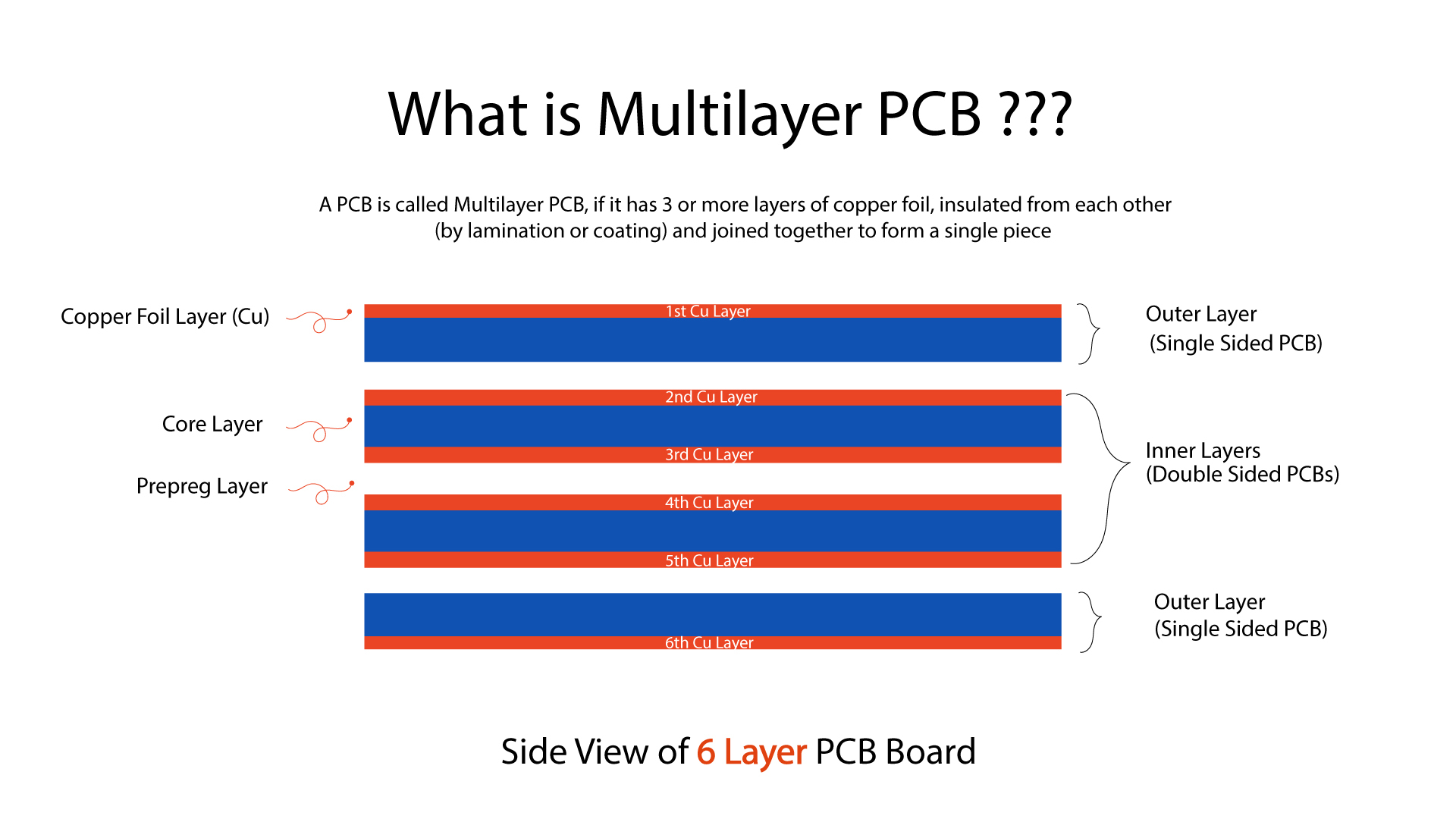
There are several types of printed circuit boards, chief among them being single-, double-, or multi-layered. While most of the simple boards in use are typically single- or double-layered, complex circuit board manufacturing is mainly multi-layered. Simple PCBs have their own advantages, but as they have only one or two layers, they cannot meet the demands of complicated circuits and high-density, close-pitch components. Modern equipment trending towards sophisticated functioning requires multi-layered printed circuit boards for superior performance. Designers and PCB fabrication services have their own grounds for multi-layered PCBs. Nevertheless, they must adhere to certain guidelines when stacking individual layers for achieving the overall PCB thickness. For this, they choose to use different materials for constructing the layers in their boards.
Advantages of Multiple Layers PCBs over Single Layer Boards
Although it is simple to assemble and use single- and double-layered boards, the size of the circuitry they can handle is rather limited. With large and complex circuitry, one or even two layers are inadequate for handling the interconnections of the components. PCB fabrication services offer designers several benefits with multiple layers for printed circuit boards. These include:
- Miniaturization
- Better Shielding and Isolation
- Improved Signal Integrity
- Better Power Handling
- Easy to Assemble
Miniaturization
When a designer translates a large complex circuitry onto a single-sided PCB, they often need a board with huge dimensions to adapt to all components and their interconnections. Although a prototype circuit board using two sides can cut the board dimensions largely, it will continue to remain unmanageable.
For practical purposes, a multi-layered board from a PCB fabrication service is more appropriate, as the designer has more space to route the interconnections between components via intermediate layers, with the components mounted on the topmost layer. This practice helps not only to shrink the physical dimensions of the board, but also allows it to retain the complexity of the circuit.
Better Shielding and Isolation
Complex circuits, being more closely spaced, require isolation and shielding to prevent cross-talk and leakage between sections, thereby permitting the board to achieve as intended functions. Isolating sections of the circuit is possible in single- and double-sided boards also, but this requires increasing the physical distance between the circuits, resulting in an increase in the overall size of the board.
In multi-layered boards, designers often introduce a power or ground layer in between to act as an isolation or shield. The introduction of an additional layer or layers does not increase the overall size of the board.
Improved Signal Integrity
For printed circuit boards working with high-speed signals, it is imperative there is no degradation of the signal as it travels through the traces on the board. If there is a mismatch between the impedance of the track and that of the signal source or the receiver, the signal will most certainly lose its integrity.
To maintain the desired impedance on one track or a pair of tracks, designers enclose them to form a proper transmission line. PCB fabrication services offering multi-layered boards is the most suitable way of creating transmission lines using adjacent layers.
Better Power Handling
Apart from handling high-speed and high-frequency signals, modern printed circuit boards may also have some tracks with high currents running through them. A printed circuit board may also have a few electronic components generating substantial amounts of heat. Miniaturized printed circuit boards often require thermal management, an important factor to keep them operational without damage.
Circuit board manufacturing services offer multi-layered PCBs that can effectively handle such power scenarios. Designers use thermal vias to transfer the heat from a hot component to the outermost layer of the board on the other side, making it easy to remove the heat. They often add a layer with heavy copper for carrying the extra current. As the entire board need not have heavy copper, this helps to optimize the cost of the printed circuit board.
Easy to Assemble
Using a single- or double-sided board for a complex circuitry may require several wire jumpers for completing the interconnections between components. The designer may also need to break up the board into different sections, and connect them via wire harnesses and connectors.
For a complex circuit, using a multi-layered printed circuit board takes care of the above problems, as the designer can place tracks on various inner layers for the interconnections. While making assembly considerably simpler, the possibilities of errors also reduces.
Multi-layered printed circuit boards have many additional advantages. Designers can distribute the interconnecting tracks among multiple layers. This results in achieving higher precision for track width and spacing. In comparison to single- or double-layered boards, multi-layered boards offer the designer considerably better flexibility, improved control over differential impedance, and higher signal integrity.
Applications of Multilayered PCB boards
Because of their higher flexibility in design, OEMs prefer using multi-layered boards widely in their electronic products. Modern PCB fabrication services offer more reliable electrical performance along with the advantages of higher stability. Multi-layered boards therefore offer a better economic performance. With the trend towards use of large-scale integrated circuits, OEMs prefer multi-layer boards for achieving high-density, high-precision, and high-level digitization in their products. With multi-layered boards featuring fine and closely spaced tracks, various types of vias like blind, buried, in-pad, and with high plate thickness to aperture ratio, circuit board manufacturing can easily meet their market demands. The above features offered by multi-layered circuit board manufacturing services has resulted in their becoming a preferred option for numerous industries including:
- Consumer Electronics
- Information Technology
- Telecommunications
- Industrial Electronics
- Medical Applications
- Military, Aerospace, and Defense
- Automotive Industry
- Security Industry
- Science and Research
Applications listed above require equipment with:
- A High Degree of Sophistication
- High Complexity
- High Reliability
- Improved Durability
- High Levels of Safety
- Use of Different Technologies
Only multi-layered printed circuit boards from modern circuit board manufacturing services can meet all the above criteria. Most applications need printed circuit boards to also comply with several international functional, operational, and safety regulations. This is only possible when using multi-layered printed circuit boards of the highest quality.
Conclusion
Several other industries also use multi-layered printed circuit boards from quality PCB fabrication services as the foundation for their products. In fact, it is impossible to realize an electronic product that does not have a multi-layered PCB assembly inside. With modern circuit board manufacturing services offering various types of multi-layered PCBs, OEMs can easily meet the requirements of different technologies and applications. For instance, they may use rigid boards made of glass-epoxy, flexible boards made of Polyimide, metal clad boards with Aluminum backing, high-frequency boards made of Teflon, and many more.



